
CURRENCY
Malaysian money is known as Ringgit, and is symbolised as RM for prices and MYR for currency exchange. One unit equals 100 sen. Banknotes are issued in denominations of RM1, RM5, RM10, RM20, RM50 and RM100, each with a specific colour. Coins are issued in cents (sen) of 5, 10, 20, and 50 pieces. They are issued by the Bank Negara Malaysia. Licensed foreign money changers can be found in all urban centres, key entry/exit points, and many shopping malls.
TRAVELLER’S CHEQUES
Traveller’s cheques are not a common form of payment in Malaysia, as ATMs are found in many locations. Should you have a traveller’s cheque on you that you have to use, look for commercial banks or authorised exchange services. Be sure to have cheques in UK Pounds, US Dollars, or Australian Dollars for a smoother transaction.
E-WALLET USE
With the rise of online banking, e-wallet apps are an increasingly popular form of money transaction in Malaysia. E-wallets that are foreign bank friendly include Masterpass, Visa Checkout, and PayPal. Increasingly popular local e-wallet options include Touch n’ Go, Grab Pay, and Boost.
BUSINESS HOURS
In all states except Kedah, Kelantan, and Terengganu, government business hours are open from Monday to Thursday, from 8am to 5.30pm, with a one hour lunch break at 12.45pm. On Fridays, lunch break is often from 12:15pm to 2.45pm to allow Muslim workers to perform their afternoon prayers. In Kedah, Kelantan and Terengganu, working days are from Sunday to Thursday instead, Fridays and Saturdays serving as the weekend. Working hours from Sunday to Wednesday are 8am to 4.45pm, and Thursdays are 8am to 4.30pm. Private sector business hours can vary, but generally are from 9am to 5pm on Monday to Friday, and 9am to 1pm on Saturday.
BANKING HOURS
On weekdays, banking hours are from 9.30am to 4.30pm, with the exception of Friday (Thursday in Kedah, Kelantan, and Terengganu) at 9.15 to 4pm. Banks are usually closed on weekends, but this may vary among individual banks.
ECONOMY
In 2019, Malaysia was recorded as the 33rd-largest economy in the world, and the third-largest in Southeast Asia behind Indonesia and Thailand with a nominal GDP of an estimated 365.3 billion (in Current International Dollars). Malaysia is the third-wealthiest ASEAN country, after Singapore and Brunei, and has an emergent industrialised market economy. Though the local currency suffered fairly significant losses against the US dollar beginning around 2014, it’s worth noting that since the election of the new government in May 2018, the ringgit has been performing fairly well, maintaining a relatively stable trade while several other ASEAN currencies faced depreciation against the USD.
Though still a primary producer of rubber, palm oil, petroleum, natural gas, and commercial hardwood, Malaysia has also steadily focused on being an industrialised nation. Malaysia is the seventh-largest electronics exporter in the world, and is a significant hub for assembly and testing. Another solid source of income is the tourism industry. Malaysia also maintains its position as the world’s top Islamic economy.
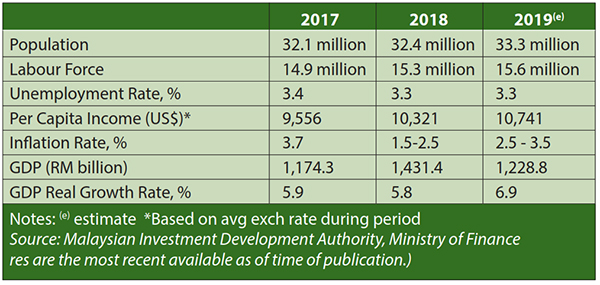
KEY ECONOMIC INDICATORS
"ExpatGo welcomes and encourages comments, input, and divergent opinions. However, we kindly request that you use suitable language in your comments, and refrain from any sort of personal attack, hate speech, or disparaging rhetoric. Comments not in line with this are subject to removal from the site. "


